Introduction
Goal-setting is an essential aspect of personal and professional growth. However, setting goals without a clear plan and measurement system can lead to a lack of direction and accountability. This is where SMART metrics come into play. SMART metrics provide a framework for setting goals that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time bound. In this article, we will explore what SMART metrics are, how they differ from Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and how they can enhance your goal-setting process.
What is a SMART Metric?
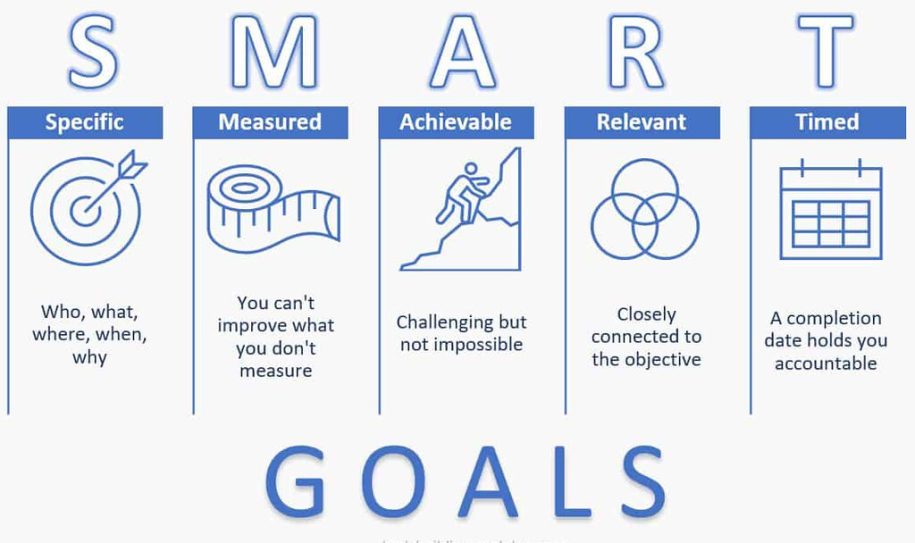
A SMART metric is a specific measurement used to track progress towards a goal. The acronym SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Each component of the SMART framework serves a purpose in ensuring that goals are well-defined and achievable.
What is the Difference Between SMART and KPI?
While both SMART metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure progress towards goals, they possess distinct differences. SMART metrics focus on individual goals, offering a framework for setting objectives that are specific and measurable. In contrast, organizations or departments use KPIs to measure overall performance.
Understanding the SMART Goal-Setting Framework
The SMART goal-setting framework provides a structured approach to goal-setting that increases the likelihood of success. Each component of the SMART framework serves a specific purpose:
Specific Goals
Specific goals are clear and well-defined. They provide a clear direction and focus for your efforts. For example, instead of setting a vague goal like “increase sales,” a specific goal would be “increase sales by 20% in the next quarter.”
Measurable Goals
Measurable goals allow you to track your progress and determine whether you are on track to achieve your objectives. They are quantifiable and provide a way to evaluate success. For example, if your goal is to increase website traffic, a measurable goal would be “increase website traffic by 30% in the next six months.”
Attainable Goals
Attainable goals are realistic and achievable. While it’s important to challenge yourself, setting goals that are too far out of reach can lead to frustration and lack of motivation. Consider your available resources and capabilities when setting attainable goals.
Relevant Goals
Relevant goals are aligned with your overall objectives and priorities. They are meaningful and contribute to your long term success. When setting relevant goals, consider how they align with your values, mission, and vision.
Time-Bound Goals
Time-bound goals have a specific deadline or timeframe. Setting a deadline provides a sense of urgency and helps to keep you accountable. Without a deadline, goals can easily be pushed aside and forgotten. Set realistic deadlines that allow for progress while maintaining a sense of urgency.

The Importance of Setting Specific Goals
Setting specific goals is crucial for effective goal-setting. Specific goals provide clarity and focus, making it easier to determine the necessary steps and resources needed to achieve them. When goals are specific, it becomes clear what needs to be done and how progress will be measured.
Specific goals also help to align efforts and resources. When everyone is clear on the specific objectives, it becomes easier to allocate resources, delegate tasks, and track progress. This alignment increases efficiency and reduces the risk of miscommunication or wasted efforts.
Furthermore, specific goals provide motivation and a sense of accomplishment. When goals are specific, progress can be tracked and celebrated along the way. This boosts morale and motivates individuals and teams to continue working towards their objectives.
SMART Performance Metrics
SMART metrics play a crucial role in measuring performance and tracking progress towards goals. By setting specific and measurable metrics, you can objectively evaluate your performance and determine whether you are on track to achieve your objectives. Also, SMART metrics provide a clear framework for measurement. They ensure that the metrics you choose are relevant and aligned with your goals. By selecting metrics that are specific and measurable, you can accurately assess your progress and make data-driven decisions. Additionally, SMART metrics allow for regular monitoring and adjustment. This way, you can identify areas of improvement, make necessary adjustments, and stay on track towards your goals.
What is SMART Metrics in Testing?
In the context of testing, SMART metrics refer to specific and measurable metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness of software testing processes. SMART metrics in testing help to assess the quality and efficiency of testing efforts, identify bottlenecks or areas of improvement, and track the progress of testing activities.
Some common SMART metrics in testing include the number of defects found, the defect detection rate, test coverage, and the percentage of test cases executed. By setting SMART metrics in testing, organizations can ensure that their testing efforts are effective, efficient, and aligned with their overall objectives.
Setting Measurable Goals Using SMART Metrics
Setting measurable goals using SMART metrics is essential for tracking progress and evaluating success. Measurable goals provide clarity and ensure that progress can be objectively assessed. By establishing specific metrics that can be tracked and measured, you can monitor your progress and make data-driven decisions.
When setting measurable goals using SMART metrics, it’s important to consider the following:
- Define the specific metrics that will be used to measure progress. These metrics should be quantifiable and directly related to the goal.
- Establish a baseline or starting point for each metric. This will allow you to track progress over time and determine whether you are moving in the right direction.
- Set realistic targets for each metric. Targets should be challenging but attainable. Consider your available resources and capabilities when setting targets.
- Regularly monitor and review your metrics. Track progress, identify areas of improvement, and make necessary adjustments to stay on track towards your goals.
By setting measurable goals using SMART metrics, you can ensure that your objectives are well-defined, progress can be tracked, and success can be objectively evaluated.

The Role of Attainability in Goal-Setting
Attainability is a key component of the SMART goal-setting framework. Setting goals that are attainable ensures that they are realistic and achievable within the given timeframe and available resources. Attainable goals are essential for maintaining motivation and preventing frustration or burnout. When setting attainable goals, it’s important to consider the following:
1. Assess your available resources and capabilities. Determine whether you have the necessary skills, knowledge, and resources to achieve the goal. If not, consider what steps need to be taken to acquire or develop the necessary resources.
2. Break down larger goals into smaller, more manageable tasks. This allows for incremental progress and prevents overwhelm. Celebrate small victories along the way to maintain motivation and momentum.
3. Seek feedback and support from others. Collaboration and support from colleagues, mentors, or subject matter experts can provide valuable guidance and assistance in achieving your goals.
By setting attainable goals, you can increase your chances of success and maintain a sense of motivation and accomplishment throughout the goal-setting process.
The Significance of Relevance in Goal-Setting
Relevance stands as a critical component within the SMART goal-setting framework, ensuring alignment with overall objectives, priorities, and values. Setting relevant goals imbues a sense of purpose, thereby contributing significantly to long-term success. When establishing such goals, several considerations come into play. Firstly, aligning goals with mission, vision, and values becomes paramount, fostering a meaningful connection and heightened motivation. Secondly, evaluating the potential impact and benefits of goal achievement aids in prioritization and resource allocation, facilitating effective progress. Lastly, continuous reassessment of goal relevance is essential, allowing for adjustments or replacements as circumstances evolve. Regular goal reviews ensure ongoing alignment with current objectives, safeguarding continued progress. Through the establishment of relevant goals, efforts are directed toward what truly matters, thereby enhancing prospects for sustained success.
What is an Example of a SMART Goal with Metrics?
An example of a SMART goal with metrics is “Increase customer satisfaction by 10% within six months.” This goal is specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound.
The specific aspect of the goal is to increase customer satisfaction, which provides clarity and focus. The goal is measurable by tracking customer satisfaction scores or feedback. It is attainable by allocating resources and implementing strategies to improve customer satisfaction. The goal is relevant because it contributes to the overall success of the business. Lastly, the goal is time-bound by setting a six-month deadline to achieve the desired increase in customer satisfaction.
By setting a SMART goal with metrics, you can provide a clear direction, track progress, and increase the likelihood of success.
Tools and Resources for Tracking and Measuring SMART Metrics
Several tools and resources are available to help track and measure SMART metrics effectively. These tools can streamline the process and provide valuable insights into your progress towards your goals. Some popular tools for tracking and measuring SMART metrics include:
1. Project management software: Tools like Trello or Jira can help you track tasks, deadlines, and progress towards your goals.
2. Analytics software: Platforms like Google Analytics or Metridev provide valuable data and insights for tracking metrics related to website traffic, conversions, and customer engagement.
3. Survey tools: allows you to collect feedback and measure customer satisfaction or employee engagement.
4. Performance dashboards: Dashboards like Tableau, Klipfolio, or Power BI can consolidate data from various sources and provide real-time metrics and visualizations.
By leveraging these tools and resources, you can streamline the tracking and measurement of SMART metrics and gain valuable insights into your progress towards your goals.
Evaluating and Adjusting SMART Goals and Metrics
Evaluating and adjusting SMART goals and metrics is a crucial step in the goal-setting process. Regular evaluation ensures that goals remain relevant, attainable, and aligned with your overall objectives. It allows you to identify areas of improvement, make necessary adjustments, and stay on track towards your goals.
When evaluating SMART goals and metrics, consider the following:
- Review your progress towards each goal. Assess whether you are on track to achieve your objectives and whether the metrics you have chosen are accurately measuring progress.
- Identify areas of improvement or potential obstacles. Determine whether there are any bottlenecks, challenges, or gaps in your current strategies or resources. Make adjustments to overcome these obstacles and improve your chances of success.
- Seek feedback and input from stakeholders. Gather input from colleagues, mentors, or other relevant individuals to gain different perspectives and insights. This feedback can provide valuable guidance and help you make informed decisions.
- Adjust goals and metrics as needed. If circumstances change or your objectives evolve, adjust your goals and metrics accordingly. Be flexible and open to adapting your strategies to ensure continued progress towards your goals.
By regularly evaluating and adjusting your SMART goals and metrics, you can maintain alignment with your overall objectives and increase your chances of success.
Conclusion: Achieving Success with SMART Goals and Metrics
Setting goals is an essential part of personal and professional growth. However, without a clear plan and measurement system, goals can lack direction and accountability. SMART metrics provide a framework for setting goals that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound.
By using the SMART goal-setting framework, you can enhance your goal-setting process and increase your chances of success. Whether you are setting personal goals, team goals, or organizational goals, the SMART framework provides a structured approach that ensures goals are well-defined, progress can be tracked, and success can be evaluated.
Remember to set specific goals that provide clarity and focus, establish measurable metrics to track progress, ensure goals are attainable and relevant, and set deadlines to maintain a sense of urgency. Regularly evaluate and adjust your goals and metrics to stay on track and make necessary improvements.
By incorporating SMART goals and metrics into your goal-setting process, you can achieve greater success and reach your full potential.
Start setting SMART goals and measuring your progress, read our article about Goal Metrics for Business Growth.
IT METRICS TO BECOME AN EXPERT













Leave a Reply